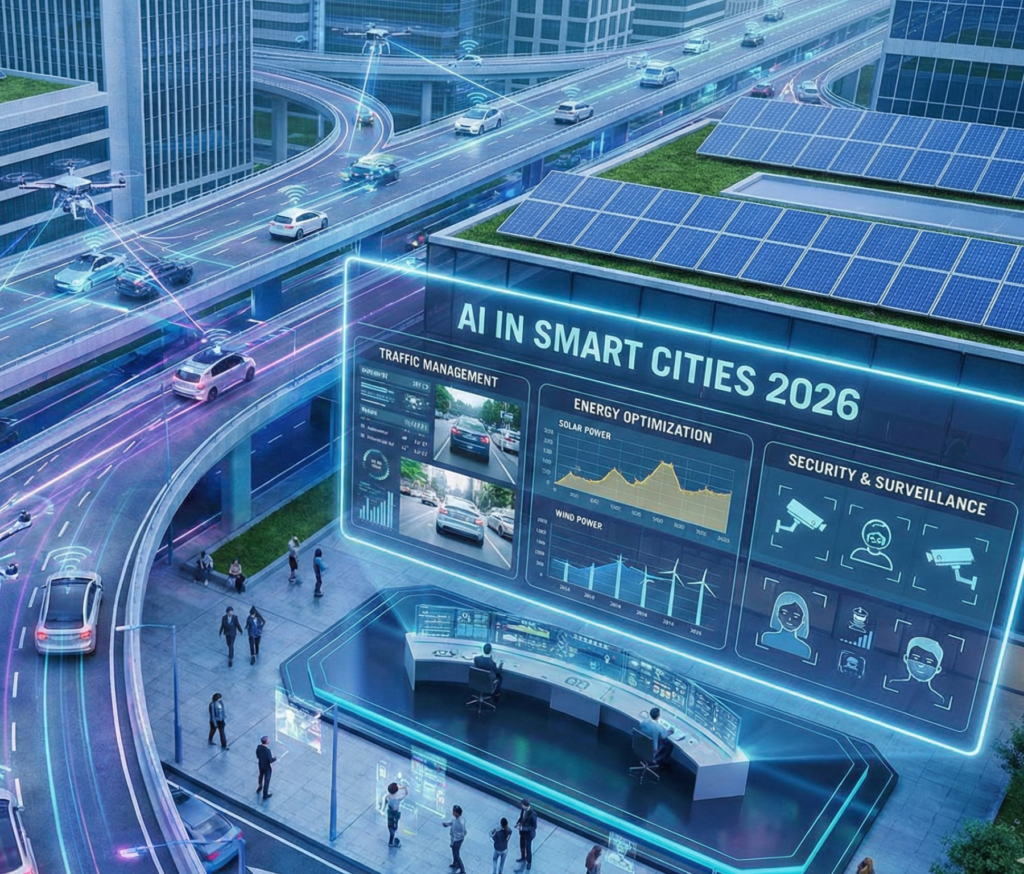
Urbanization is accelerating globally. By 2026, more than half of the world’s population lives in cities, putting immense pressure on infrastructure, transportation systems, energy grids, and public safety mechanisms. To manage this complexity, governments and municipalities are increasingly adopting artificial intelligence.
AI in Smart Cities 2026 is no longer a futuristic concept — it is an operational reality. Artificial intelligence is being integrated into traffic control systems, energy management grids, surveillance infrastructure, waste systems, water supply networks, and emergency response platforms.
Smart cities leverage AI to collect, process, and analyze massive volumes of real-time data, enabling faster decision-making, improved efficiency, and better public services.
This in-depth report explores how AI powers traffic management, energy optimization, security systems, urban planning, and the future of intelligent cities.
What Is a Smart City?
A smart city uses digital technologies, sensors, and artificial intelligence to optimize urban operations.
Core components include:
- IoT sensors
- Data analytics platforms
- Cloud computing infrastructure
- AI decision-making systems
- Integrated communication networks
Major global tech companies like IBM and Microsoft support smart city infrastructure projects worldwide.
AI in Traffic Management
Traffic congestion is one of the biggest urban challenges. AI-powered systems analyze real-time data from:
- Traffic cameras
- GPS signals
- Public transport networks
- Road sensors
AI systems dynamically adjust traffic signals to reduce congestion.
How AI Optimizes Traffic Flow
| AI Function | Impact on Traffic |
|---|---|
| Real-Time Signal Adjustment | Reduces congestion |
| Predictive Traffic Modeling | Prevents bottlenecks |
| Smart Parking Systems | Reduces search time |
| Accident Detection | Faster emergency response |
AI reduces travel time and fuel consumption.
AI and Public Transportation
AI improves:
- Bus route optimization
- Metro scheduling
- Ride-sharing algorithms
- Passenger demand forecasting
Autonomous vehicle testing is also integrated into smart city systems.
AI in Energy Management
Energy demand in cities fluctuates constantly.
AI helps optimize:
- Electricity distribution
- Renewable energy integration
- Smart grid management
- Demand forecasting
Smart Grid Optimization
AI-powered smart grids balance:
- Supply and demand
- Renewable energy inputs
- Power outages
- Load distribution
| Energy Application | AI Benefit |
|---|---|
| Solar Integration | Efficient energy storage |
| Demand Prediction | Reduced blackout risk |
| Consumption Monitoring | Lower energy waste |
AI reduces carbon emissions and increases sustainability.
AI in Urban Security and Surveillance
Security is a major pillar of smart cities.
AI-driven surveillance systems analyze:
- Video feeds
- Facial recognition
- Suspicious activity detection
- Crowd behavior monitoring
Advanced systems often rely on cloud AI infrastructure provided by companies like Google.
AI Security Capabilities
| Security Feature | AI Function |
|---|---|
| Facial Recognition | Identify persons of interest |
| Anomaly Detection | Detect unusual activity |
| Predictive Policing | Identify high-risk areas |
| Emergency Alerts | Faster public communication |
AI improves response time during emergencies.
AI in Waste Management
Smart waste systems use sensors to:
- Monitor bin fill levels
- Optimize garbage collection routes
- Reduce fuel costs
AI scheduling improves sanitation efficiency.
AI in Water Management
Water scarcity is a global issue.
AI systems monitor:
- Pipeline leaks
- Water consumption patterns
- Flood risk predictions
Predictive models prevent water wastage and infrastructure damage.
AI in Disaster Management
Smart cities use AI for:
- Earthquake detection
- Flood prediction
- Emergency evacuation planning
- Weather pattern analysis
AI enhances disaster preparedness and reduces casualties.
Economic Impact of AI in Smart Cities
AI adoption improves:
- Operational efficiency
- Infrastructure lifespan
- Public safety
- Sustainability metrics
Economic Benefits
| Sector | Financial Impact |
|---|---|
| Traffic Optimization | Reduced fuel costs |
| Energy Efficiency | Lower utility expenses |
| Security Systems | Reduced crime-related costs |
| Waste Management | Lower operational spending |
AI implementation saves billions in long-term infrastructure costs.
AI and Data Infrastructure
Smart cities depend on:
- High-speed connectivity
- Cloud data centers
- IoT device networks
- Real-time analytics
Data governance is critical for privacy protection.
Challenges of AI in Smart Cities
Despite benefits, challenges include:
- Data privacy concerns
- Cybersecurity risks
- High implementation costs
- Ethical concerns in surveillance
- Integration complexity
Governments must ensure responsible AI deployment.
AI in Smart Cities: India’s Perspective
India is investing in smart city initiatives under national development programs.
Focus areas include:
- Traffic monitoring in major metros
- Renewable energy integration
- Digital surveillance infrastructure
- Smart public transportation
AI-driven solutions are being implemented in major cities to manage urban growth.
Global Smart City Leaders
Countries investing heavily in smart city AI include:
- Singapore
- United Arab Emirates
- South Korea
- United States
These cities implement advanced AI-driven urban management systems.
Future of AI in Smart Cities Beyond 2026
Future developments may include:
- Fully autonomous public transport
- AI-driven energy-neutral buildings
- Emotion-aware public safety systems
- Blockchain-integrated city governance
Smart cities will evolve into fully integrated digital ecosystems.
AI in Smart Cities vs Traditional Urban Systems
| Factor | Traditional System | AI Smart System |
|---|---|---|
| Traffic Signals | Fixed timing | Real-time adaptive |
| Energy Grid | Static distribution | Predictive balancing |
| Security Monitoring | Manual review | Automated detection |
| Waste Collection | Fixed schedule | Demand-based routing |
AI dramatically increases efficiency.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
AI supports:
- Reduced carbon emissions
- Optimized energy usage
- Cleaner transportation
- Smarter resource management
Sustainability is central to smart city development.
Final Conclusion
AI in Smart Cities 2026 is reshaping how urban environments operate. From traffic optimization and renewable energy management to security surveillance and disaster response, artificial intelligence is becoming the backbone of modern city infrastructure.
Smart cities are no longer experimental projects — they are strategic investments in economic growth, sustainability, and public safety.
As AI continues evolving, urban systems will become more predictive, efficient, and autonomous. Governments and technology companies will collaborate further to build cities that are safer, cleaner, and more intelligent.
For Digital Technologia, this topic positions your AI & Tools category as forward-thinking, research-driven, and globally relevant.